One of the mainstays of psychotherapy is the idea that talking about your emotions—or even writing about them—can help you to regulate them. Mindfulness-based approaches from Buddhism offer similar outcomes—the idea is that if you are “mindful,” or aware, of your feelings, then they won’t seem as strong. Until recently, it was not well understood […]
The post Does labeling your feelings help regulate them? appeared first on Emotion News.
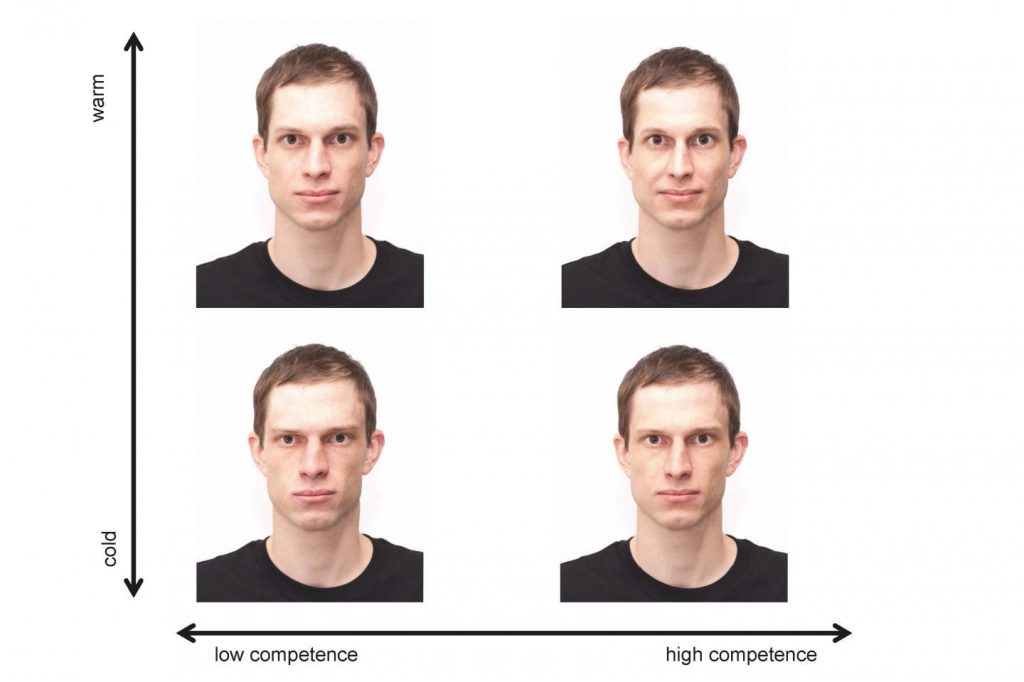 People are often excluded from social groups. As researchers from the University of Basel in Switzerland report in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, whether uninvolved observers find this acceptable or not may depend on the facial appearances of those excluded. The exclusion of cold and incompetent looking people is more likely to be accepted.
People are often excluded from social groups. As researchers from the University of Basel in Switzerland report in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, whether uninvolved observers find this acceptable or not may depend on the facial appearances of those excluded. The exclusion of cold and incompetent looking people is more likely to be accepted. By Melanie Tannenbaum for Scientific American
By Melanie Tannenbaum for Scientific American